
The three key unmet needs in dermatology disease
management are “limited treatment options",
"ineffectiveness of available therapies" and "poor adherence to treatment".

Development of NCE and new formulations with better efficacy
Improves transdermal efficiency to increase efficacy, simplifies treatments and reduces adverse effects
Better aesthetic acceptability and physical sensation of use

Innovative technology platform that can be customized to form a series of products based on specific APl and disease

Significantly improve the efficiency of transdermal, while leveraging long-lasting effect, and reduce the number of doses

No need to use dressing, easy to use, transparent and beautiful appearance, improve patient compliance

Good clinical data demonstrating excellent skin tolerability

Creates a breathable barrier to protect lesions while promoting skin healing
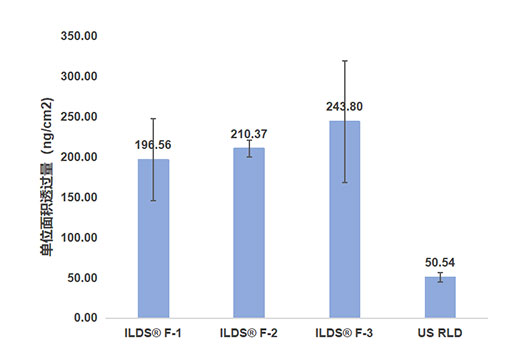
IDT-003 (almost insoluble in water, solubility about 0.00477g/L)
Transdermal diffusion tester, model TK-24BL
Isolated skin from Parmesan minipigs’ back
saline, 32±0.5°C, 400 rpm agitation
in-house developed ILDS® formulation (three different prescriptions)
U.S. reference drug (US RLD)
300mg±10 mg
6h
Determination of drug content retained in skin samples after exfoliation

Pro-xylane
Transdermal diffusion tester, model TK-24BL
Isolated skin from Parmesan minipigs’ back
saline, 32±0.5°C, 400 rpm agitation
in-house developed ILDS® formulation
U.S. reference drug (US RLD)
300mg±10 mg
6h
Determination of drug content retained in skin samples after exfoliation

Hyaluronic acid labeled by rhodamine-B (RhB), molecular weight 200,000-300,000 Da
Transdermal diffusion tester, model TK-24BL
Isolated skin from Parmesan minipigs’ back
saline, 32±0.5°C, 400 rpm agitation
in-house developed ILDS® -RhB-HA (0.1%)formulation
RhB-HA (0.1%)
300mg±10 mg
6h
Skin samples were exfoliated and frozen sectioned, and the exogenous HA transdermal condition was determined qualitatively by measuring red fluorescence through fluorescence microscopy